Mice Matter
Our campaign aims to educate people about the sensitivity of mice and how this cannot be accommodated in laboratories.
Mice deserve the same consideration as other animals! Our campaign debunks the myths around the use of mice in research. Find out more:
Why should you care about mice?
Even if an animal is small, if we are unfamiliar with how they live in the wild or if they are not popular with the public, they should still be treated with consideration and care, just as larger, more familiar animals are, such as dogs and cats. Mice are intelligent animals, who feel pain in a comparable way to people.
Although millions of mice each year are killed in traps or poisoned, Animal Aid’s main focus is on the approximately three million mice who are bred, harmed and killed each year in UK laboratories.
How do wild mice live?
Wild mice may eat 200 small meals each night, visiting many feeding sites. Wild mice are eaten by other animals, so they prefer to stay close to cover and in contact with solid objects, to feel secure. Mice are nocturnal, so they see best in very low light. Smell is the mouse’s most important sense, used to find and assess both their food and also predators. Mice are highly social and usually live in family units.
Male mice will ‘sing’ to females. A female mouse may make more than 150 trips to gather material for her nest. Mice are born blind, deaf and almost hairless, but they grow and develop fast so that by 4 weeks of age, they are able to make brief trips from their nest, usually with a parent. The mice are usually sexually mature at about 6 weeks.
How mice live, and suffer, in laboratories
Laboratory cages can never replicate the complexity of life experienced by a mouse in the wild. No matter how ‘enriched’ a cage is, caged animals cannot control where they go, burrow, escape unpleasant things or explore. There is ample evidence that animals in laboratories, including mice, suffer from their day-to-day living conditions. Even moving and cleaning cages causes stress in animals. Additionally, prey animals like mice tend to hide signs of pain or distress, which makes them completely unsuited to the time-constrained laboratories in which they are kept.
Mice are often kept in containers, stacked on racks, possibly with thousands of animals per room; the scope for suffering is enormous. In 2021, many terrible incidents of suffering were reported in laboratories in Great Britain:
Read about these incidents
- 4 mice died after receiving injections containing fragments from a faulty pestle and mortar.
- A mouse became trapped when their cage was changed. They were found dead 5 days later.
- A ‘transport error’ resulted in 17 mice being left in a transport box with limited food and water for 6 days.
- A mouse had overgrown teeth which were not noticed at weaning. They were later found dead.
- A mouse was kept alive even after they lost more weight than ‘allowed’ as the limit of what was considered ‘humane’.
The various strains of mice used in laboratories are acknowledged to be ‘associated’ with certain clinical conditions. Examples of this suffering include:
- Increased fluid around the brain,
- Abnormally small eyes,
- An absence of one or both eyes,
- Misaligned teeth,
- Skin lesions due to excessive grooming,
- Heart problems,
- Seizures.
Experiments
The range of conditions and diseases which are induced and inflicted upon mice could fill countless pages, but include the following:
- Genetically modified mice bred in an attempt to ‘model’ human diseases such as Alzheimer’s.
- The injection of cancer cells into a mouse’s body to try to cause cancer.
- Mice undergoing damage to their brains to induce strokes.
- Mice being ‘tested’ in water mazes, on spinning rods and with hot plates.
Species differences
As well as being inhumane, research with mice is unscientific, as animal experiments do not reliably predict what will happen in humans. Differences between mice and humans include:
- Mouse and human livers activate or neutralise cancer-causing substances ‘quite differently’.
- ‘the mouse lung is considerably different in structure from the human lung’.
- The rate of energy produced per gram of bodyweight is seven times greater in mice than humans.
- Some common human diseases, such as mental illness and Alzheimer’s, do not occur naturally in mice.
- Mice cannot vomit.
Mice Victims of Charity
Our Victims of Charity campaign raises public awareness of the cruel and pointless animal experiments funded by some medical research charities.
Examples of experiments from our Victims of Charity campaign
Here are some examples from Victims of Charity which show how mice are treated in laboratories, and the dreadful protocols to which they are subjected:
November 2014 – The British Heart Foundation (BHF) helped to fund dreadful animal experiments which included mice deliberately being given heart attacks. The anaesthetised mice had their chests opened up and then the blood flow to their hearts was blocked for between five and 30 minutes, in order to induce a heart attack.
This method, conducted on young mice, was completely different to the way in which heart attacks in people often occur due to complex, longstanding problems. A review of animal ‘models’ of damage to the heart explained how the ‘typical’ patient suffering a heart attack is a man, aged 64, with several illnesses and how ‘the majority of animal disease models are performed on young, healthy male animals in the absence of any co-morbid illnesses’
December 2014 – Experiments involving Motor Neurone Disease Association-funded researchers where GM mice were bred to suffer limb paralysis, anxiety, loss of bodyweight and motor dysfunction.
March 2015 – CRUK co-funded a study, two phases of which involved mice. In one phase nude mice had human cancer cells injected under their skin. The cancer was allowed to grow for three weeks before some mice were given treatment. The other phase involved a group of GM mice being poisoned for six months with a chemical traditionally used in the leather and motor fuel industries. This was done to cause cancer.
September 2015 – The Alzheimer’s Society co-funded a series of experiments wherein GM mice had injected into their abdomen each day, for eight weeks, a drug used to treat diabetes in humans. These poor animals then underwent a regime of highly stressful behavioural tests, following which they were anaesthetised and had holes drilled in their skulls so that electrodes could record their brain activity.
October 2016 – A research centre, founded with money from Arthritis Research UK, provided a grant to support experiments on a number of ten-week old, male mice. The experiments involved operating on the mice to intentionally damage one knee of each animal. Animals previously mutilated in this way had been killed over a period of time (between two to eight weeks after the operation) and the injured joint sliced, labelled with a substance and examined.
February 2017 – Cancer Research UK provided ‘generous financial support’ for experiments where mice had cancer cells injected into their hearts. The male mice received prostate cancer cells and the female mice received breast cancer cells. These cells were made to glow so that tumour growth could be identified while the animals were alive. The animals were killed at various times after the injections into their hearts; the method of killing is not stated.
Ways in which mice are ‘tested’ in laboratories
Morris Water Maze –
This forces mice (innately strictly terrestrial animals) to swim in a tank of water until they locate a surface platform on which to rest. The platform is subsequently hidden, and mice must remember its location, at the same time as trying to escape through frantic swimming.
Rotor-rod ™ –
This machine has rods, onto which animals are placed. The rods are then rotated and the mice must then keep ‘walking’ forward in order not to fall off the rod, as it rotates towards them. The machine’s manufacturer describes how it ‘Utilizes the “fear of falling” instinct as a natural motivator’.
Self-righting –
A group of researchers who used GM mice to ‘model’ a type of motor neuron disease described how the ‘endpoint’, when mice would be killed, would be when the mouse had a ‘loss of self-righting ability within 10 seconds of being placed on the back, or weight loss of >30% for 72 hours.’
They describe in chilling detail how, ‘Mice were provided with wet mashed food in their cages at the first sign of hind limb paralysis. At this point the cage bedding material was changed to paper towel to reduce dust and allow for easier locomotion.’
Hot-plate test –
During the experiment the animal is placed on a surface consisting of a heated plate. The mouse is timed until s/he does certain things such as licking their paw or jumping, in an attempt to escape the heat.
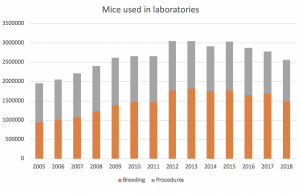
How has the use of mice changed over time?
This graph shows two categories of mice: those who were used to create or breed genetically altered animals who were not used in further procedures and those who were used in experimental procedures. The graph shows how the ratio has changed, and the total has generally increased, over the years.
How can I get involved?
- Speak out for mice when you learn about their use in experiments. There are actions you can take on our Victims of Charity website,
- Use our graphic on social media,
- Order Mice Matter leaflets.